Burton Lab
Research
Pathogenesis and drug discovery using transgenic zebrafish models.
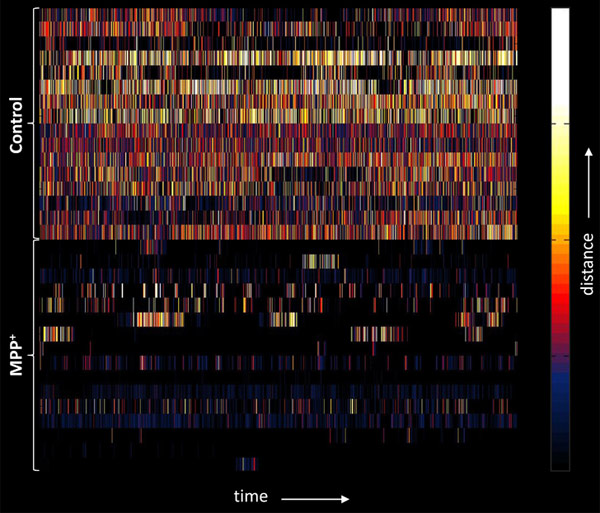
We have developed zebrafish models of neurological diseases and assays for their analysis. By taking advantage of the transparency of larval zebrafish and their unique suitability for high throughput screening, we aim to gain insights into disease mechanisms in vivo and to discover novel chemical modifiers of disease phenotypes.
- Farrell, T. C., Cario, C. L., Milanese, C., Vogt, A., Jeong, J.-H., Burton, E. A. (2011) Evaluation of spontaneous propulsive movement as a screening tool to detect rescue of Parkinsonism phenotypes in zebrafish models. Neurobiology of Disease. 44(1), 9-18.
- Cario, C. L., Farrell, T. C., Milanese, C. and Burton, E. A. (2011). Automated measurement of zebrafish larval movement. The Journal of Physiology. 589(15), 3703-8.
- Horowitz, M., Milanese, C., Di Maio, R. Hu, X., Montero, L. M., Sanders, L., Tapias, V., Sepe, S., van Cappellen, G., Burton, E. A., Greenamyre, J. T., Matsroberardino, P. G. (2011) Single-cell redox imaging demonstrates a distinctive response of dopaminergic neurons to oxidative insults. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling. 15(4), 855-71
- Bai, Q., Sun, M., Stolz, D. B., Burton, E. A. (2011). The major isoform of zebrafish P0 is a 23.5kDa myelin glycoprotein expressed in selected white matter tracts of the central nervous system. Journal of Comparative Neurology. 519(8),1580-96
- Bai, Q. and Burton, E. A. (2009). Cis-acting elements responsible for dopaminergic neuron-specific expression of zebrafish slc6a3 (dopamine transporter) in vivo are located remote from the transcriptional start site. Neuroscience. 164(3),1138-51
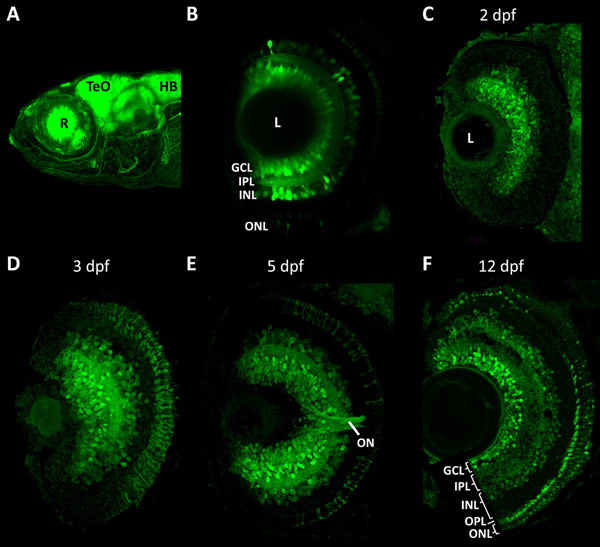
- Bai, Q., Wei, X., and Burton, E. A. (2009). Expression of a 12kb promoter fragment derived from the zebrafish enolase-2 gene in the zebrafish visual system. Neurosci Lett. 449(3), 252-7.
- Bai, Q., Garver, J. A., Hukriede, N. A., Burton, E. A. (2007). Generation of a transgenic zebrafish model of Tauopathy using a novel promoter element derived from the zebrafish eno2 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 35 (19), 6501-16
- Bai, Q., Mullett, S. J., Garver, J. A., Hinkle, D. A., and Burton, E. A. (2006). Zebrafish DJ-1 is evolutionarily conserved and expressed in dopaminergic neurons. Brain Res 1113, 33-44.
Gene-environment interactions in neurodegenerative diseases.
By using viral gene transfer to modulate gene expression, we are investigating how genes modify cellular responses to environmental triggers in mammalian models of Parkinsonism.
- Cannon, J., Sew, T., Montero, L., Burton, E. A., and Greenamyre, J. T. (2011). Pseudotype-dependent lentiviral transduction of astrocytes or neurons in the rat substantia nigra. Experimental Neurology. 228(1), 41-52
- Niranjan, A., Fellows, W., Stauffer, W., Burton, E. A., Hong, C. S., Lunsford, L. D., Kondziolka, D., Glorioso, J. C., and Gobbel, G. T. (2007). Survival of transplanted neural progenitor cells enhanced by brain irradiation. Journal of Neurosurgery 107, 383-391.
- Hong, C.-S., Goins, W. F., Goss, J. R., Burton, E. A. and Glorioso, J. C. (2006) Herpes simplex virus RNAi and neprilysin gene transfer vectors reduce accumulation of Alzheimer’s disease-related amyloid-b peptide in vivo. Gene Therapy 13, 1068-1079
- Kwon, H., Bai, Q., Baek, H. J., Felmet, K., Burton, E. A., Goins, W. F., Cohen, J. B., and Glorioso, J. C. (2006). Soluble V Domain of Nectin-1/HveC Enables Entry of Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 (HSV-1) into HSV-Resistant Cells by Binding to Viral Glycoprotein D. Journal of Virology 80, 138-148.
- Burton, E. A., Hong, C.-S. and Glorioso, J. C. (2003). The stable 2.0kb LAT intron of HSV-1 does not function in trans as a repressor of ICP0 function. Journal of Virology, 77, 3516-3520.
- Burton, E. A., Glorioso, J. C. and Fink, D.J. (2003). Progress and prospects in gene therapy: Parkinson’s disease. Gene Therapy, 10, 1721-1727